Introduction
The Cisco IOS Zone Based Firewall is one of the most advanced form of Stateful firewall used in the Cisco IOS devices. The zone based firewall (ZBFW) is the successor of Classic IOS firewall or CBAC (Context-Based Access Control). Cisco first implemented the router-based stateful firewall in CBAC where it used ip inspect command to inspect the traffic in layer 4 and layer 7.
Even though ASA devices are considered as the dedicated firewall devices, Cisco integrated the firewall functionality in the router which in fact will make the firewall a cost effective device. The zone based firewall came up with many more features that is not available in CBAC. The ZBFW mainly deals with the security zones, where we can assign the router interfaces to various security zones and control the traffic between the zones. Also the traffic will be dynamically inspected as it passes through the zones. In addition to all the features which is available in classic IOS firewall, Zone based firewall will support Application inspection and control for HTTP, POP3, Sun RPC, IM Applications and P2P File sharing.
For advanced configuration of IOS Zone Based Firewall refer http://yadhutony.blogspot.in/2013/08/zone-based-firewall-advanced_4036.html
Zone Based Firewall Vs CBAC
| CBAC |
Zone Based Firewall |
| Interface Based Configuration |
Zone Based Configuration |
| Controls Inbound and Outbound access on an interface |
Controls Bidirectional access between zones. |
| Uses inspect statements and stateful ACLs |
Uses Class-Based Policy language |
| -Not supported- |
Support Application Inspection and Control |
| Support from IOS Release 11.2 |
Support from IOS Release 12.4 (6) T |
- This document will guide you to configure a basic Zone Based Policy Firewall in an IOS router. Here I am going to divide the entire configuration into logical sets and finally will combine them to the get the full configuration.
ZBFW Configuration Procedure
The below are the configuration tasks that you need to follow:
- Configure Zones
- Assign Router Interfaces to zones
- Create Zone Pairs
- Configure Interzone Access Policy (Class Maps & Policy Maps)
- Apply Policy Maps to Zone Pairs
Configuration Scenario
Figure 1.
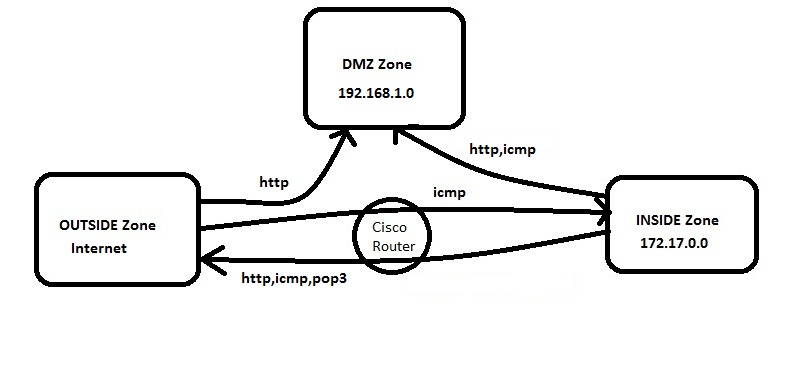
In this example we have three zones.
- Inside Zone – Private LAN
- DMZ Zone – DMZ hosts
- Outside Zone – Internet
Here I am defining a rule set for our ZBFW:
1. From Inside to Outside –http,icmp and pop3 is allowed
2. From Outside to Inside –icmp is allowed
3. From Inside to DMZ –http and icmp is allowed
4. From Outside to DMZ –http is allowed
Default Rules of Zone Based Firewall
- Interzone communication is Denied, traffic will be denied among the interfaces that are in the different zones unless we specify a firewall policy.
- Intrazone communication is Allowed, traffic will flow implicitly among the interfaces that are in the same zone.
- All traffic to Self zone is Allowed
Self Zone is created automatically by the router while we create the other zones in a Zone Based Firewall.
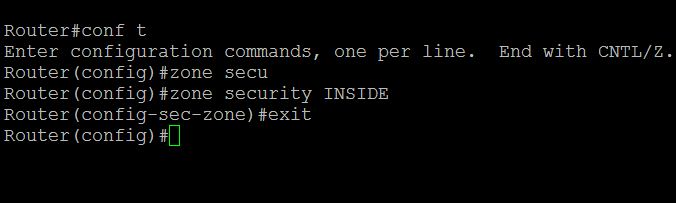
Task 1 : Configure Zones
In this example (refer Figure 1) we have three zones. Inside ,Outside, DMZ.
To configure zones in a router, connect the router via putty or console, switch to the global configuration mode and type the command as below:
Router(config)#zone security INSIDE
Router(config)#zone security OUTSIDE
Router(config)#zone security DMZ
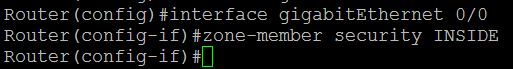
Task 2 : Assign Router Interfaces to Zones
We have to assign the router interface to a particular zone. Here I am going to assign Gigabyte Ethernet 0/0 to INSIDE zone , Ge0/1 to OUTSIDE zone and Ge0/2 to DMZ zone.
To achieve this we have to go to the particular interface and attach that interface to the zone.Type the command as below:
Router(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/0
Router(config-if)#zone-member security INSIDE
Router(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/1
Router(config-if)#zone-member security OUTSIDE
Router(config)#interface gigabitEthernet 0/2
Router(config-if)#zone-member security DMZ
Now if you try to ping a zone from another zone the traffic will be denied because of the default firewall policy.
Task 3 : Create Zone Pairs
Zone pairs are created to connect the zones. If you want to make two zones to communicate you have to create Zone pairs. DO NOT create zone pairs for non-communicating zones. In our scenario the traffic flows between :
- INSIDE to OUTSIDE
- OUTSIDE to INSIDE
- OUTSIDE to DMZ
- INSIDE to DMZ
So we need to create four zone pairs. To create zone pairs the command is as follows.
Router(config)#zone-pair security IN-TO-OUT source INSIDE destination OUTSIDE
Router(config)#zone-pair security OUT-TO-IN source OUTSIDE destination INSIDE
Router(config)#zone-pair security OUT-TO-DMZ source OUTSIDE destination DMZ
Router(config)#zone-pair security IN-TO-DMZ source INSIDE destination DMZ

Task 4 : Configure Interzone Access Policy
Interzone Access policy is the key part of a Zone based firewall where we classify the traffic and apply the firewall policies. Class map and Policy map configurations are carried out during this task.
Class Maps : This will classify the traffic
Policy Maps : This will decide the ‘fate’ of the traffic
Class Map Configuration
Class map sort the traffic based on the following criteria 1.) Access-group 2.) Protocol 3.) A subordinate class map. In our scenario I am sorting the traffic based on access group. So first we need to create an ACL and associate it with the class map.
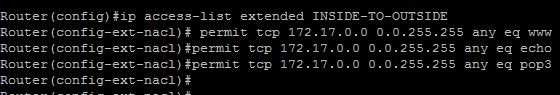
a.) Class Map for INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE
Router(config)#ip access-list extended INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp 172.17.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq www
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp 172.17.0.0 0.0.255.255 any eq pop3
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit icmp 172.17.0.0 0.0.255.255 any
Router(config)#class-map type inspect match-all INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE-CLASS
Router(config-cmap)#match access-group name INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE
or
[ you can group the protocols as below:
class-map type inspect match-any INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE-CLASS
description Allowed_Protocol_From_INSIDE_to_OUTSIDE
match protocol https
match protocol dns
match protocol udp
match protocol tcp
match protocol pop3
match protocol smtp
match protocol icmp ]
b.) Class Map for OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE
Router(config)ip access-list extended OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit icmp any 172.17.0.0 0.0.255.255
Router(config)#class-map type inspect match-all OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE-CLASS
Router(config)#match access-group name OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE
c.) Class Map for OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ
Router(config)#ip access-list extended OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp any 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 eq www
Router(config)#class-map type inspect match-all OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ-CLASS
Router(config)#match access-group name OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ
d.) Class Map for INSIDE-TO-DMZ
Router(config)#ip access-list extended INSIDE-TO-DMZ
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit tcp 172.17.0.0 0.0.255.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 eq www
Router(config-ext-nacl)#permit icmp 172.17.0.0 0.0.255.255 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255
Router(config)#class-map type inspect match-all INSIDE-TO-DMZ-CLASS
Router(config-cmap)#match access-group name INSIDE-TO-DMZ

Policy-Map Configuration
Policy-Maps will apply the firewall policy to the class map that is configured previously. Three actions can be taken aganist the traffic with the policy-map configuration:
- Inspect : Dynamically inspect the traffic.
- Drop : Drop the traffic
- Pass : Simply forward the traffic.
There will be a drop policy, by default, at the end of all policy maps.
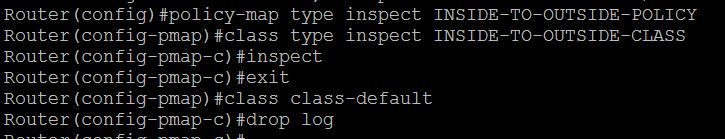
a.) Policy-map for INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE
Router(config)#policy-map type inspect INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE-POLICY
Router(config-pmap)#class type inspect INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE-CLASS
Router(config-pmap)#inspect
Router(config-pmap)#class class-default
Router(config-pmap)#drop log
b.) Policy-map for OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE
Router(config)#policy-map type inspect OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE-POLICY
Router(config-pmap)#class type inspect OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE-CLASS
Router(config-pmap)#pass
Router(config-pmap)#class class-default
Router(config-pmap)#drop log
c.) Policy-map for OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ
Router(config)#policy-map type inspect OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ-POLICY
Router(config-pmap)#class type inspect OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ-CLASS
Router(config-pmap)#inspect
Router(config-pmap)#class class-default
Router(config-pmap)#drop log
d.) Policy-map for INSIDE-TO-DMZ
Router(config)#policy-map type inspect INSIDE-TO-DMZ-POLICY
Router(config-pmap)#class type inspect INDISE-TO-DMZ-CLASS
Router(config-pmap)#pass
Router(config-pmap)#class class-default
Router(config-pmap)#drop log
Task 5 : Apply policy maps to zone pairs
Now we have to attach the policy maps to the zone pairs that we have already created. The command is as follows:
Router(config)#zone-pair security IN-TO-OUT source INSIDE destination OUTSIDE
Router(config-sec-zone-pair)#service-policy type inspect INSIDE-TO-OUTSIDE-POLICY
Router(config)#zone-pair security OUT-TO-IN source OUTSIDE destination INSIDE
Router(config-sec-zone-pair)#service-policy type inspect OUTSIDE-TO-INSIDE-POLICY
Router(config)#zone-pair security OUT-TO-DMZ source OUTSIDE destination DMZ
Router(config-sec-zone-pair)#service-policy type inspect OUTSIDE-TO-DMZ-POLICY
Router(config)#zone-pair security IN-TO-DMZ source INSIDE destination DMZ
Router(config-sec-zone-pair)#service-policy type inspect INSIDE-TO-DMZ-POLICY

There we finish the basic configuration of a zone based firewall.
Troubleshooting
You can use the below commands to perform some basic troubleshooting and verification.
a.) Show commands
show class-map type inspect
show policy-map type inspect
show zone-pair security
b.) Debug Commands
debug policy-firewall detail
debug policy-firewall events
debug policy-firewall protocol tcp
debug policy-firewall protocol udp
Advanced Zone Based Firewall Configuration
Here you can find some examples of advanced Zone Based Firewall configuration.
1. Advanced Zone Based Firewall Configuration : http://yadhutony.blogspot.in/2013/08/zone-based-firewall-advanced_4036.html
2. IOS Content Filtering : http://yadhutony.blogspot.in/2013/02/cisco-ios-local-content-filtering.html
3. P2P and IM Application control : http://yadhutony.blogspot.in/2012/11/how-to-block-p2p-traffic-on-cisco-router.html
You can visit http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/ios-xml/ios/sec_data_zbf/configuration/15-1s/sec-zone-pol-fw.html for more details.
Thank you for viewing this document.